Linode Writer's Formatting Guide
Traducciones al EspañolEstamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.



Write Guides for Linode
This guide provides templates and guidelines to use when creating or updating a guide for Linode Docs.
Updates, improvements, and bug fixes to Linode documentation are always welcome through GitHub via pull requests (PRs) or issues.
Through our Write For Linode program, authors can contribute new guides and be paid for their work. We ask that interested authors apply to the program with one or more writing samples so that we can evaluate your work. To learn more about the program and to complete an application, please visit our Write For Linode program page.
General Layout
Linode Guides & Tutorials are written in Markdown. Our documentation site uses Hugo, a static site generator. Hugo-specific Markdown formatting notes are given further below.
Markdown files for guides are stored under the docs/guides/ content directory. This content directory is then further subdivided into categories for different technical topics. New guides should be placed with a category that they most closely align with. For example, if you are writing a new guide on the Apache web server, it would be placed under docs/guides/web-servers/apache/.
A new subdirectory is created for each guide. This subdirectory should contain a file called index.md, which will be where the guide’s Markdown is written to. For example, if your guide’s title is My Apache Guide, then you would create its Markdown file at docs/guides/web-servers/apache/my-apache-guide/index.md.
A Hugo archetype is available to create new Markdown files. For example, if you wanted to create the My Apache Guide example guide, you could run this command from inside your cloned docs repository:
hugo new -k content docs/guides/web-servers/apache/my-apache-guide/index.mdHeader
Linode Guides & Tutorials store metadata and other information in a YAML header at the top of every page. Use the template below for your own guide.
- File: Author Submission
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16--- slug: url-slug-for-your-guide title: "Title of Your Guide (appears in H1)" title_meta: "Title of Your Guide (appears in meta title tag)" description: 'Two to three sentences describing your guide.' og_description: 'Two to three sentences describing your guide when shared on social media.' keywords: ['list','of','keywords','and key phrases'] license: '[CC BY-ND 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0)' authors: ["Linode"] published: 2023-03-07 modified_by: name: Linode external_resources: - '[Link Title 1](http://www.example.com)' - '[Link Title 2](http://www.example.net)' ---
If you’re updating an existing guide in our repository, you may also notice a deprecated field in the header. This defaults to false, and setting it to true inserts a pre-written message near the beginning stating that the guide is no longer maintained. Typically, this will be used on guides specific to applications or distributions that have reached End of Life (EOL).
Introduction
Introductions should be concise; explain what the goal of the guide is and why. If you’re introducing new software to the system, include a brief description and link to its official website whenever possible.
Before You Begin
The Before You Begin section is an area for basic prerequisites a reader should know or have completed before proceeding further in your guide. Use the example below and edit as needed:
- File: Author Submission
1 2 3 4 5## Before You Begin 1. If you have not already done so, create a Linode account and Compute Instance. See our [Getting Started with Linode](/docs/products/platform/get-started/) and [Creating a Compute Instance](/docs/products/compute/compute-instances/guides/create/) guides. 1. Follow our [Setting Up and Securing a Compute Instance](/docs/products/compute/compute-instances/guides/set-up-and-secure/) guide to update your system. You may also wish to set the timezone, configure your hostname, create a limited user account, and harden SSH access.
Include a Note about Root or Non-Root users
- File: Guides Written for a Non-Root User
1 2 3{{< note >}} This guide is written for a non-root user. Commands that require elevated privileges are prefixed with `sudo`. If you’re not familiar with the `sudo` command, see the [Users and Groups](/docs/guides/linux-users-and-groups/) guide. {{< /note >}}
- File: Guides Written for a Root User
1 2 3{{< note >}} The steps in this guide require root privileges. Be sure to run the steps below as `root` or with the `sudo` prefix. For more information on privileges, see our [Users and Groups](/docs/guides/linux-users-and-groups/) guide. {{< /note >}}
Paragraph Structure
Guides should be split into cohesive sections which flow from one sequence of events to the next. Each section title should be styled with an H2 heading element, and each subsection with an H3 heading so that scanning the In This Guide left sidebar should give the reader an overview of what will be done in the guide. Capitalize each noun, adjective, verb and adverb in the article title, H2 and H3 headers.
Each subsection should be split into numbered steps as shown below.
For example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32## Using MySQL 1. Log in to MySQL as the root user: ```command mysql -u root -p ``` 1. When prompted, enter the root password. ### Create a New MySQL User and Database 1. In the example below, `testdb` is the name of the database, `testuser` is the user, and `password` is the user’s password. ```command create database testdb; grant all on testdb.* to 'testuser' identified by 'password'; ``` 1. Exit MySQL. ```command exit ``` ### Create a Sample Table 1. Log back in as `testuser`: ```command mysql -u testuser -p ```
How to Use Markdown Formatting for Linode Style
Abbreviations and Acronyms
Upon first mention of a new concept or software, use the full name or term, then note the abbreviation or acronym in parenthesis beside it. The abbreviation/acronym can then be used in the article from that point. For example: Lightweight Resource/Provider (LWRP).
Introduce new terms in italics with a * on either side of the term:
1This guide covers how to install Git, a *version control system*.
Output: This guide covers how to install Git, a version control system.
Bold and Italics
Use a Bold font weight for buttons, menu selections and anything that requires emphasis or that you want to stand out to the reader. Italicize new terms and concepts the first time they are used.
| Syntax | Output |
|---|---|
**bold** | bold |
*italics* | italics |
Commands
Commands that are not inline with paragraph text should be displayed with the command shortcode. This shortcode renders the command in a monospaced font with a light or dark background and a copy-to-clipboard button. Unlike other shortcodes (e.g. content, note, caution, etc), the command shortcode should be referenced with Markdown’s code fence syntax.
Command shortcode example
1 2 3```command sudo systemctl restart apache2 ```
The above command shortcode is rendered with a light grey background by default:
sudo systemctl restart apache2Multiline commands
The command shortcode can accept multiple lines if more than one command needs to be displayed:
1 2 3 4```command sudo systemctl restart apache2 sudo journalctl -u apache2 ```
The above command shortcode is rendered as:
sudo systemctl restart apache2 sudo journalctl -u apache2Command with title
The
titleparameter can be used to specify a title that displayed above a command shortcode. This can be useful to label the server or workstation that a reader should execute the command on. For example, some guides instruct the reader to set up multiple servers. Specifying a title can disambiguate which server a given command should be run on.1 2 3 4 5 6 7```command {title="Web server"} sudo systemctl restart apache2 ``` ```command {title="Database server"} sudo systemctl restart mysql ```
The above command shortcodes are rendered as:
Web serversudo systemctl restart apache2Database serversudo systemctl restart mysqlCommand with dark background
The
classparameter can be used to specify that a command should be displayed with a dark background:1 2 3```command {class="dark"} sudo systemctl restart apache2 ```
The above command shortcode is rendered as:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Commands (Deprecated Syntax)
In some existing guides, you may see commands displayed without the command shortcode. In these instances, the commands are simply indented with a tab or four spaces in the Markdown source text. For example:
1 2 3Run the following command to restart Apache: sudo systemctl restart apache2
The older (tab or four space-indent) syntax should not be used for new content. The code shortcode renders a copy-to-clipboard button for the reader’s convenience, and the old syntax does not provide this feature.
Inline Commands
Inline commands should be denoted by backticks.
1Update your system by running `yum update`.
Output: Update your system by running yum update.
Example IP Addresses
Example IPs should use the documentation address blocks given in IETF RFC 5737. These are:
- 192.0.2.0/24
- 198.51.100.0/24
- 203.0.113.0/24
External Resources/More Information
If you wish to provide links to external sites for the user to review after going through your guide, do so using the external_resources parameter in the page header. This will automatically appear as a text block with links at the bottom of the page.
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
Extend Markdown Using Shortguides
Using shortcodes, it is possible to extend a Markdown file with another. For common tasks such as basic software installation, consider using the content shortcode. This allows our library to maintain consistent and up to date installation instructions for frequently used tools such as Python, MySQL, and Docker.
Markdown files intended to be inserted into multiple guides are called shortguides. To create a shortguide, create a directory with the name of your shortguide anywhere within docs/, and then create an index.md within the directory for your content (e.g. example-shortguide-name/index.md).
Inserting headless: true in the front matter will hide the guide from the site navigation as well as the search index.
When using the content shortcode in a guide to embed a shortguide, the shortcode will take the name of your guide’s directory (e.g. example-shortguide-name) as a parameter. A shortguide can be within a different part of the docs hierarchy from the guide that embeds it, so the guide directory name exists within a global namespace of all shortguides in the repository. In other words, two different shortguides can’t use the same directory name.
To use an image in a shortguide, add the image to your shortguide’s directory and then use the image shortcode to embed it:
- File: sample_embedding_guide/index.md
1{{< image src="image-name.png" alt="image alt label" title="image title" >}}
Example Usage
The following shortguide describes how to install Python via Miniconda. Create a directory named install_python_miniconda and filed named index.md within it:
- File: install_python_miniconda/index.md
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30--- title: "Install Python with Miniconda" description: 'A shortguide that shows how to install Python via Miniconda.' keywords: [] license: '[CC BY-ND 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0)' authors: ["Author's FirstName LastName`"] published: 2023-03-07 modified: 2023-03-07 modified_by: name: Linode headless: true show_on_rss_feed: false --- <!-- Installation instructions for Python 3. --> 1. Download and install Miniconda: ```command curl -OL https://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh bash Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86.64.sh ``` 1. You will be prompted several times during the installation process. Review the terms and conditions and select "yes" for each prompt. 1. Check your Python version: ```command python --version ```
To use this shortguide in another guide, use the following syntax:
- File: sample_embedding_guide/index.md
1{{< content "install_python_miniconda" >}}
Files
Use the file shortcode to present code examples, code snippets, and other text file contents in a guide. This shortcode renders the file content with line numbering, a specified filepath, syntax highlighting, and line highlighting. Unlike other shortcodes (e.g. content, note, caution, etc), the file shortcode should be referenced with Markdown’s code fence syntax.
File with filepath
1 2 3 4 5```file {title="/path/to/file.html"} <div> Sample file text </div> ```
The above file shortcode is rendered as:
- File: /path/to/file.html
1 2 3<div> Sample file text </div>
File with language/syntax highlighting
A code language or syntax can be defined with the
langparameter to set how the text is displayed. A list of supported languages can be found on GitHub.1 2 3 4 5```file {title="/path/to/file.html" lang="html"} <div> Sample file text </div> ```
The above file shortcode is rendered as:
- File: /path/to/file.html
1 2 3<div> Sample file text </div>
File with starting line specified
If your file snippet represents the middle of a file, you can use the
linenostartto specify that the line numbering to the left of the snippet should start at a number other than 1:1 2 3 4 5```file {title="/path/to/file.html" lang="html" linenostart="11"} <div> Sample file text </div> ```
The above file shortcode is rendered with line numbers 11, 12, and 13 instead of 1, 2, and 3:
- File: /path/to/file.html
11 12 13<div> Sample file text </div>
File with highlighted lines
The
hl_linesparameter can be used to highlight certain lines within the file. The parameter is a space-separated list of strings. Ranges of lines can also be specified:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11```file {title="client/src/Header.js" lang="react" linenostart="11" hl_lines="4-6 9"} import React from 'react'; function Header() { return ( <header> Example header text </header> ); } export default Header; ```
The above file shortcode highlights lines 4 through 6 and line 9:
- File: client/src/Header.js
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19import React from 'react'; function Header() { return ( <header> Example header text </header> ); } export default Header;
Using file shortcodes within lists
If using a file shortcode in a list, each line of the shortcode should start at the indentation level of the list. For example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 91. List item 1 1. List item 2 ```file {title="/path/to/file.html" lang="html"} <div> Sample file text </div> ```
Files (Deprecated Syntax)
In some existing guides, you may see this older shortcode syntax for displaying a file:
1 2 3 4 5{{< file "path/to/file.html" html >}} <div> Sample file text </div> {{< /file >}}
This is equivalent to:
1 2 3 4 5```file {title="/path/to/file.html" lang="html"} <div> Sample file text </div> ```
The older syntax should not be used for new content. While they are rendered with the same presentation by Hugo, they are not displayed the same in the GitHub.com UI. When viewing a Markdown file in the library on GitHub, the newer code fence shortcode syntax will have enhanced styling, compared with the older shortcode syntax.
File Paths and File Names
Inline file paths and file names should be formatted as inline code blocks.
| Syntax | Output |
|---|---|
Navigate to `/var/www/html`. | Navigate to /var/www/html. |
Headings
Headings should be written in title case and can be up to 3 levels deep.
| Syntax | Output |
|---|---|
## Section title (h2) | Section title (h2) |
### Subsection (h3) | Subsection (h3) |
#### Subsection (h4) | Subsection (h4) |
Images
Images can add value to the surrounding text by providing context or additional meaning. In most cases, images within documentation take the form of screenshots or diagrams, though occasionally other types of images may be necessary.
Image format: All images should a PNG (.png) or a JPEG (.jpg or .jpeg).
Image size: Images are displayed in their original size, up to the maximum width of the content area. If an image’s width is larger than the width of the content area, the image is scaled down to fit within the content area and a user can click on the image to view it in a modal.
To add an image to a guide, first move it the same directory as the guide or shortguide. Then, enter the following Markdown syntax at the location you wish the image to appear:
1
- Alt text: This should be a description of the image and is rendered within the image’s
alttag. It is used for screen readers and other accessibility features. - Filename: The name of the file. Filenames cannot contain spaces and should use hyphens (-) and underscores (_) instead.
- Title text: This is the text that appears as a tooltip when a user hovers over the image. If no title is entered, the alt text is used in the
titletag. In most cases, a specific title tag is not needed.
Image Recommendations
The height of our images, especially screenshots, should be as minimal as possible. This is to avoid screenshots taking up a lot of vertical space within our documentation, which often results in visually breaking up content that otherwise should appear together. Our Cloud Manager favors vertically stacked fields and options, which can make it difficult to minimize the height of our screenshots. Use your best judgement when determining what part of the UI is needed to convey the required information.
Avoid including too much detail or information within an image. Many images are used to either show a result of an action (like displaying a web page) or are used to supplement instructions asking the reader to perform an action (like click a button). Images that show too much may confuse the reader or otherwise call attention to details that aren’t important to the task at hand. In practice, this means not taking a screenshot of the entire application or browser window and instead focusing only on the UI elements related to the instructions or text.
Also, ensure that all identifying attributes such as names and IP addresses are removed, obfuscated, or replaced with example text, such as example_user or an IP address from the 192.0.2.0/24 range. This aligns with a previous recommendation of only providing necessary detail and it keeps the writer’s personal information from being shown to readers. This may involve using the browser’s built-in development tools to manually replace values or delete information.
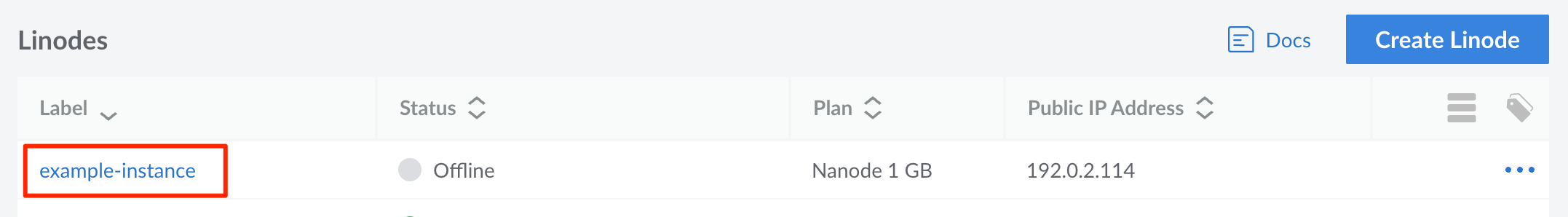
Example Wide Image
Since this image is larger than the width of the content, the image is scaled to fit. When the image is clicked, a modal appears that displays the image at a larger size.
This example image might be used to supplement instructions asking the reader to select a Compute Instance. Instead of taking a screenshot of the entire page in the Cloud Manager, the area has been cropped to just include relevant information. In addition, a red outline has been used to highlight the UI element that corresponds with the action the reader should perform.
1

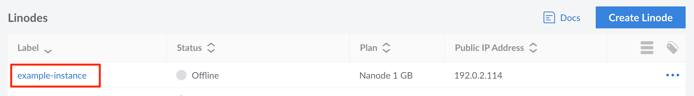
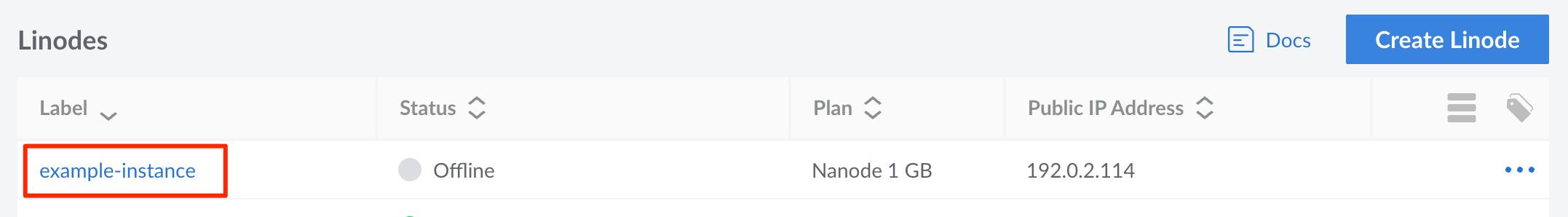
Example Narrow Image
Smaller images should be displayed using their true pixel size. When taking screenshots within some software on some operating systems, the pixel size is increased (likely to account for the operating system’s scaling). For instance, taking a screenshot with the Skitch tool on macOS doubles the pixel count. In these cases, use another image editing tool (like macOS’s built in preview) to scale down the image to match the intended pixel width.
1
Key Combinations
When instructing a reader to press hotkeys or other combinations of keys, enclose each individual key within a kbd html element as shown in the example below.
1Use <kbd>Ctrl</kbd> + <kbd>C</kbd> to copy text.
Output: Use Ctrl + C to copy text.
Links
Internal links to other Linode guides should be relative, starting at /docs/, and external links should be formatted as shown below and use HTTPS URLs whenever possible.
- Internal link example:
[Getting Started](/docs/products/platform/get-started/) - External link example:
[Apache HTTP Server Documentation](https://httpd.apache.org/docs/)
Lists
Ordered Lists
Ordered lists are numbered and should be used to denote a series of steps or sequential items. Use the following guidance when creating ordered lists:
Longer lists that may change and where nested content is possible:
These lists should use lazy numbering (by appending a
1.to each step regardless of the actual step number). There should also be two spaces between the numbering and the text (see Nested Content Within Lists).1. Step 1 1. Step 2 1. Step 3Short lists that remain static with no nested content:
Optionally, you can use true numbering when a list is likely to remain short and static during its lifecycle. Provided there is no nested content, use a single space between the number and the text.
1. Step 1 2. Step 2 3. Step 3
Unordered Lists
Unordered lists are bulleted and should be used for any collection of items that do not necessarily need to be ordered. These lists should be formatted by appending a - to the beginning of each step.
Lists where nested content is possible:
Use three spaces between the bullet character (
-) and the text. (see Nested Content Within Lists).- Item A - Item B - Item CLists with no nested content:
Provided there is no nested content, you can use a single space between the bullet character and the text.
- Item A - Item B - Item C
Nested Content Within Lists
To remain consistent across all of our guides, nested content should be indented four spaces and a blank line should be used above and below the content. Our Markdown processor assumes nested content starts directly below the first character in the text of the list item above it. With this in mind, it’s important to indent the text portion of the list item to match that four space indent. In practice, there should be two spaces after the number (for ordered lists) and three spaces after the bullet for unordered lists. If this spacing is not respected, the nested content may not render properly.
- Ordered list (
1.): Use two spaces after the number. - Unordered list (
-): Use three spaces after the bullet.
- Item A
This sentence is nested under *Item A*.
- Item B
```command
This command is nested under *Item B*.
```
- Item CNote Shortcode
The note shortcode is used to display a note to the reader.
1 2 3{{< note >}} This is an example note. {{< /note >}}
Parameters
The shortcode accepts the following parameters:
| Parameter | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
type | Identifies the note as one of 4 types: | |
"secondary" | A muted note. | |
"primary" | (DEFAULT) A note or tip related to the surrounding content. This is the default type if no type is specified. | |
"warning" | A note to take certain precautions. | |
"alert" | An important note that should not be skipped over. | |
title | String | Sets the title of the note. |
noTitle | boolean | Does not apply a default title to the note. Defaults to false. |
isCollapsible | boolean | Sets the note as collapsible. The note must have a title defined. Defaults to false. |
respectIndent | boolean | This is only used for older note shortcodes ({{< note >}}) that have been converted to the newer shortcode. By default, content between the shortcode tags is rendered using .InnerDeindent, which allows the shortcode to respect the indentation of any parent elements (such as lists). When set to false, .Inner is used instead, which does not de-indent the content and does not respect the indentation of parent elements. Defaults to true. |
Note Types
There are four unique types of notes:
Secondary (
type="secondary", title defaults to “Note”)Note This is an example of a secondary note with inline code (
sudo nano), a link ( Linode Documentation), and a command shortcode:sudo apt updatePrimary (type is unset or
type="primary", title defaults to “Note”)Note This is an example of a primary note with inline code (
sudo nano), a link ( Linode Documentation), and a command shortcode:sudo apt updateWarning (
type="warning", title defaults to “Warning”)Warning This is an example of a warning note with inline code (
sudo nano), a link ( Linode Documentation), and a command shortcode:sudo apt updateAlert (
type="alert", title defaults to “Important”)Important This is an example of an alert note with inline code (
sudo nano), a link ( Linode Documentation), and a command shortcode:sudo apt update
Custom Title
Each note can also have a custom title, which is set using the title parameter.
1 2 3{{< note title="Custom title" >}} This is an example note with a custom title. {{< /note >}}
No Title
Additionally, you can specify that the note should have no title by using noTitle=true. This causes the default title to not display.
1 2 3{{< note noTitle=true >}} This is an example note with no title. {{< /note >}}
Collapsible
Additionally, a note can also be collapsible by setting isCollapsible=true (defaults to false). This hides the body of the note and displays a collapse/expand icon.
1 2 3{{< note title="This is a collapsible note with a custom title" isCollapsible=true >}} This content is hidden until the user expands the note. {{< /note >}}
Indentation
Content within the opening and closing note shortcode tags must respect the expected indentation of any parent elements, such as list items. Since content within a list is indented (using 4 spaces), the content of a note shortcode must be indented by the same number of spaces.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7- First list item. {{< note >}} This content appears within the first list item and, as such, respects its indentation. {{< /note >}} - Second list item.
If this indentation is not respected, which should only be the case for older note shortcodes made before this change, the following option is set: respectIndent=false. If one of these is encountered when editing an existing guide, remove respectIndent=false and properly indent the shortcode.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7- First list item. {{< note respectIndent=false >}} This content appears within the first list item but does not respect its indentation. {{< /note >}} - Second list item.
Numerical Values
| 1-10 | Greater than 10 |
|---|---|
| Use words (one, two, three, etc.) | Use numerical digits (11, 22, 33). |
Sentence Spacing
Use single spaces between sentences; do not double-space.
Tables
You can create tables using standard Markdown syntax. Additionally, you can embed a Markdown table within the table shortcode for additional functionality.
1 2 3| Column Header 1 | Column Header 2 | | -- | -- | | **Example** | This is an example of text in the second column. |
| Column Header 1 | Column Header 2 |
|---|---|
| Example | This is an example of text in the second column. |
Column Text Alignment
To align text within a table, modify the second row. This row separates the header from the body of the table and can be used for additional metadata, like text alignment.
- Left aligned: Default behavior (if there is a need to be explicit, use
| :-- |) - Center aligned:
| :--: | - Right aligned:
| --: |
1 2 3| Left-Aligned Text | Center-Aligned Text | Right-Aligned Text | | -- | :--: | --: | | Example | Example | Example |
| Left-Aligned Text | Center-Aligned Text | Right-Aligned Text |
|---|---|---|
| Example | Example | Example |
Table Shortcode
The table shortcode can be used to add additional functionality to Markdown tables. By default, it adds a scrollbar when the table width is larger than the content area. This means that it can accommodate wide tables with lots of columns. It also adds alternating row background colors so that tables are easier to parse.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7{{< table >}} | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | | -- | -- | -- | | **Row 1** | Example | Example | | **Row 2** | Example | Example | | **Row 3** | Example | Example | {{< /table >}}
| Column Header | Column Header | Column Header |
|---|---|---|
| Row 1 | Example | Example |
| Row 2 | Example | Example |
| Row 3 | Example | Example |
Fixed First Column
If you are creating a wide table and need the first column to be fixed when scrolling, use the “first-sticky” class.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7{{< table class="first-sticky" >}} | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | | **Row1**| Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | | **Row2**| Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | | **Row3**| Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | {{< /table >}}
| Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header | Column Header |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Row1 | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Row2 | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Row3 | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
Tabs
Using a tabbed interface allows you to separate content into user-selectable tabs. This can be used to provide specific instructions for different versions of a software application (like MySQL 5.7 or 8), different operating systems (like macOS, Windows, or a Linux distribution), or different user tools (like the Cloud Manager, Linode CLI, or Linode API).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8{{< tabs >}} {{< tab "Tab 1" >}} The content only appears when *Tab 1* is selected. {{< /tab >}} {{< tab "Tab 2" >}} When *Tab 2* is selected, this content appears. {{< /tab >}} {{< /tabs >}}
When a user selects a tab, the first item in each tab set that has a matching title is also selected. This means that if multiple tab sets are on a page, each with the same items, the user only needs to select an item within one tab set and all tab sets will show that item.
When a tab is selected, a tab parameter string appears in the URL along with the title of all selected tabs. For instance, if Tab 2 is selected in the tab sets above, ?tabs=tab-2 is appended to the URL. This allows the URL to be saved or shared, keeping the same tabs selected on the page.
Terminal Output
Output from terminal commands should be displayed with the output shortcode:
1 2 3```output Hello world! ```
The above shortcode is rendered as:
Hello world!Here’s an example of a command (using the code shortcode) and its output (using the output shortcode) displayed together:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7```command echo "Hello world!" ``` ```output Hello world! ```
The above shortcodes are rendered as:
echo "Hello world!"Hello world!Terminal Output (Deprecated Syntax)
In some existing guides, you may see this older shortcode syntax for displaying terminal output:
1 2 3{{< output >}} Hello world! {{< /output >}}
This is equivalent to:
1 2 3```output Hello world! ```
The older syntax should not be used for new content. While they are rendered with the same presentation by Hugo, they are not displayed the same in the GitHub.com UI. When viewing a Markdown file in the library on GitHub, the newer code fence shortcode syntax will have enhanced styling, compared with the older shortcode syntax.
Author Pages
Profile pages for authors are listed at https://www.linode.com/docs/authors/. These are automatically generated from the authors frontmatter of the guides in the library. These pages list all of the guides that an author has published in the docs library.
Docs contributors can create author pages by following these steps:
authors frontmatter of the guides you have written. The second step shows you how to add custom biographical information to the profile page.On the guides you have written, update the
authorsfrontmatter to reference your name. This should be formatted like:1authors: ["FirstName LastName"]
(Optional) Create a new directory and Markdown file for your author page under the
docs/authorsdirectory in the docs repository. The new directory should named after you, with uppercase letters replaced by lower case, and spaces replaced by a dash. For example, an author with the nameNathan Smithwould have a new profile page created atdocs/authors/nathan-smith/_index.md.Note Note that the Markdown file is named_index.md, notindex.mdA Hugo archetype is available to create new author pages. For the example author
Nathan Smith, you would run this command to create the Markdown file for their profile page:hugo new -k authorpage docs/authors/nathan-smith/_index.mdThe template that will be created looks like:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8--- title: "Nathan Smith" link: "" email: "" description: "The Linode documentation library's profile page and submission listing for Nathan Smith" --- A short biography of the docs author/contributor. This biography text is displayed above a listing of their published docs/content.
You can set an email, website link, and short meta description in the frontmatter of this file. You can also update the body of the file with a biography of the author. This biography will be displayed above the author’s published guides listing.
Legal Information
COPYRIGHT OWNERSHIP. Writer agrees that the Work is being created by the writer for the Linode Guides & Tutorials repository and that each form of Work is being created by the writer as a “work made for hire” under the United States Copyright Act and, at all stages of development, the Work shall be and remain the sole and exclusive property of Linode. At Linode’s sole, absolute and unfettered discretion, Linode may make any alterations to the Work.
CREDIT. Nothing contained in this Agreement shall be deeded to require Linode to use the Work, or any part thereof, in connection with Linode Guides & Tutorials or otherwise. Credit for the Work shall read, “Contributed by [writer’s name].”
PAYMENT. Upon publication of a submission to the Linode Guides & Tutorials Repository, the writer will be paid the sum agreed to by email by both Linode and the author. Author may choose payment either in the form of a credit to their Linode account, a hardcopy check, or as an electronic payment via PayPal.
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
This page was originally published on